You’re about to embark on an exploration of Venus like never before. In this article, we’ll take you on a journey through the fascinating world of high-resolution imaging and cartographic insights. Get ready to delve into the mesmerizing details of Venus, as we uncover the secrets hidden within its intricate maps and uncover the beauty of this enigmatic planet. So, fasten your seatbelts and prepare to be amazed by the wonders of Mapping Venus!
Exploring Venus
Venus, the second planet from the Sun, has long captivated the curiosity of scientists and space enthusiasts alike. Over the years, several exploration missions have been conducted to unravel the mysteries of this enigmatic planet. These missions have not only provided valuable insights into the composition and structure of Venus but have also paved the way for high-resolution imaging and cartographic advancements.
Past exploration missions
In the past, numerous missions were sent to Venus with the primary objective of studying its geology and atmospheric conditions. The first successful exploration mission was the Soviet Union’s Venera 7, which landed on the Venusian surface in 1970. This marked the beginning of a series of Venera missions that aimed to gather data about the planet’s surface, temperature, and pressure. The knowledge gained from these early missions laid the groundwork for future exploration endeavors.
Purpose of mapping Venus
The mapping of Venus serves multiple purposes. Firstly, it helps us gain a better understanding of the geology and topography of the planet. By mapping its surface features, scientists can identify and study various landforms such as mountains, valleys, and impact craters. Additionally, mapping Venus aids in the identification of potential volcanic hotspots and tectonic activity, which further contributes to our understanding of the planet’s unique geological history.
Importance of high-resolution imaging
High-resolution imaging plays a crucial role in mapping Venus, as it allows scientists to capture detailed and accurate images of the planet’s surface. This level of imaging resolution is significant because it helps reveal intricate features and provides insight into the geological processes that have shaped Venus over millions of years. From studying the distribution of volcanic activity to identifying potential changes in the surface landscape, high-resolution imaging has proven to be an invaluable tool for exploring and understanding Venusian geology.
Understanding Venusian Geology
Venus, often referred to as Earth’s “twin” due to its similar size, has a vastly different geology. To comprehend its unique geological characteristics, scientists have extensively studied the composition, structure, and surface features of this mysterious planet.
Composition and structure of Venus
Venus is primarily composed of a rocky mantle and a dense iron core, similar to Earth. However, its atmosphere sets it apart from our home planet. Venus’ atmosphere is predominantly composed of carbon dioxide, with clouds of sulfuric acid. This thick atmosphere creates a runaway greenhouse effect, resulting in scorchingly high surface temperatures and pressures.
Volcanic activity on Venus
One of the most prominent features on Venus’ surface is its extensive volcanic activity. Unlike Earth, which has plate tectonics that contribute to the distribution of volcanic activity, Venus’ volcanism is thought to be driven by internal heating caused by the planet’s slow cooling process. The lava flows and volcanic structures observed on Venus provide valuable insights into the planet’s geologic evolution and help scientists understand the processes shaping its surface.
Impact craters and tectonic features
While Venus lacks the extensive plate tectonics that lead to the formation of large mountain ranges seen on Earth, it still exhibits tectonic features such as rift valleys and coronae. Additionally, the planet is adorned with numerous impact craters, which give us information about the age of the surface and the frequency of impact events. By carefully mapping these features, scientists can piece together the history of Venus and gain a deeper understanding of its geologic past.
Mapping the Venusian surface
Mapping the surface of Venus has been a complex task, given the planet’s thick atmosphere and extreme conditions. However, advancements in imaging technologies and mapping techniques have made remarkable progress in this field. By utilizing these tools and techniques, scientists have been able to create detailed maps of Venus that provide valuable data on surface features, geologic structures, and potential areas of scientific interest.
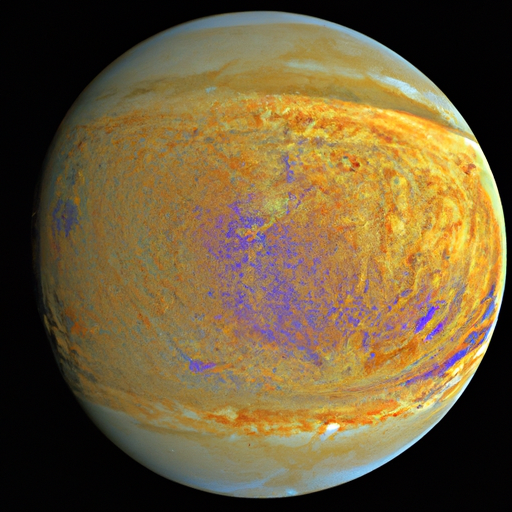
Technological Advancements in Mapping
Advancements in mapping techniques and imaging technologies have revolutionized our ability to explore and understand Venus. These advancements have been instrumental in capturing high-resolution images of the planet’s surface and analyzing its geologic features.
Evolution of Venus mapping techniques
From the early missions like Venera to present-day endeavors, the techniques used for mapping Venus have undergone significant evolution. Early missions relied on simple imaging cameras to capture a limited view of the planet’s surface. Today, sophisticated radar systems and spectrometers are employed, allowing scientists to obtain more detailed and accurate data about Venus’ geological characteristics.
High-resolution imaging technologies
One of the most significant breakthroughs in mapping Venus has been the development of high-resolution imaging technologies. These technologies, such as synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and laser altimetry, enable scientists to capture images with exceptional clarity and precision. High-resolution imaging not only helps identify surface features but also aids in the study of geological processes, such as volcanic eruptions and tectonic activities, on Venus.
Development of cartographic tools
Alongside advancements in imaging technologies, the development of cartographic tools has played a vital role in mapping Venus. Sophisticated software and algorithms are now available to process and analyze the vast amounts of data collected during exploration missions. These tools allow scientists to create accurate maps, analyze topographic features, and monitor changes in the Venusian surface over time.
Venus Express Mission
Among the notable missions dedicated to exploring Venus, the Venus Express spacecraft stands out as a testament to technological innovation and scientific progress. Launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2005, the Venus Express mission aimed to study the planet’s atmosphere, surface, and overall geology.
Overview of the Venus Express spacecraft
The Venus Express spacecraft was equipped with a range of instruments designed to gather data about Venus’ atmosphere and surface. These instruments included a spectrometer, a camera, and a radar system. The spacecraft orbited Venus for over eight years, collecting invaluable data that contributed significantly to our understanding of the planet.
Mission objectives and instruments
The primary objective of the Venus Express mission was to study the atmosphere of Venus, focusing on its composition, dynamics, and chemistry. The data collected by the spacecraft’s instruments provided insights into the planet’s thick clouds, atmospheric circulation patterns, and the presence of trace gases. Additionally, high-resolution imagery obtained by the mission aided in mapping the Venusian surface and identifying geological features.
High-resolution imaging achievements
The Venus Express mission achieved several notable milestones in high-resolution imaging. The spacecraft’s camera captured detailed images of the Venusian surface, showcasing its complex geological features. These images helped scientists identify volcanic structures, impact craters, and tectonic features. The data obtained from the mission’s high-resolution imaging played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of Venusian geology and its geological history.

Magellan Mission
Another significant mission that greatly contributed to the mapping and exploration of Venus was the Magellan mission, undertaken by NASA. This mission, launched in 1989, used radar mapping techniques to uncover the secrets hidden beneath the thick Venusian clouds.
Overview of the Magellan spacecraft
The Magellan spacecraft was specifically designed to map the surface of Venus using synthetic aperture radar (SAR). Equipped with a sophisticated radar system, the spacecraft orbited Venus for over four years, collecting radar images and data that provided critical insights into the planet’s surface features.
Mapping techniques employed
Unlike other missions that relied on optical imaging, the Magellan mission utilized radar mapping techniques to penetrate through the dense Venusian clouds. Synthetic aperture radar allowed the spacecraft to capture detailed images of Venus’ surface, revealing its topographic features in unprecedented clarity. By mapping the planet’s surface using radar, scientists were able to study Venusian geology without any interference from its opaque atmosphere.
Cartographic insights obtained
The Magellan mission yielded a plethora of cartographic insights about Venus. By carefully analyzing the radar images obtained by the spacecraft, scientists were able to identify and map various geological features such as mountains, valleys, and impact craters. These insights provided valuable information about the planet’s geologic history, surface evolution, and the activity of processes like volcanism and tectonics.
Venera Missions
The Venera missions, conducted by the Soviet Union from the 1960s to the 1980s, were instrumental in expanding our knowledge about Venus and its geology. These missions faced numerous challenges, but they paved the way for future exploration and cartographic discoveries.
Overview of Venera missions
The Venera missions were a series of Soviet space probes sent to explore Venus. These missions included both flybys and landers, with the primary objective of studying the planet’s atmosphere, surface, and overall geologic characteristics. Although some of the early lander missions were unsuccessful, later missions provided groundbreaking data about Venus.
Challenges of mapping Venus in early missions
Mapping Venus during the early Venera missions was a challenging task. The planet’s thick atmosphere obstructed optical imaging, making it difficult to capture clear images of its surface features. Furthermore, the oppressive conditions on Venus, with temperatures exceeding 900 degrees Fahrenheit and pressures over 90 times that of Earth, posed significant challenges for the landers and their instruments.
Important cartographic discoveries
Despite these challenges, the Venera missions made several important cartographic discoveries. The successful landings on Venus provided crucial information about the planet’s surface composition, temperature, and atmospheric conditions. The missions also captured images and collected data on the presence of rocks, soil, and atmospheric gases, which helped scientists develop a better understanding of Venus’ distinct geology and its divergence from Earth.
Venus as a Planet
Understanding Venus as a planet is essential for comprehending its geology and mapping its surface. While there are some similarities between Venus and Earth, there are also distinct differences that make Venus a fascinating subject of study.
Comparisons with Earth
Venus is often referred to as Earth’s “twin” due to its similar size and proximity to our planet. However, the similarities end there. While Earth’s atmosphere supports life and fosters a habitable environment, Venus’ atmosphere is primarily composed of carbon dioxide with clouds of sulfuric acid, creating a harsh and inhospitable environment. Venus’ surface temperatures reach extreme levels, hot enough to melt lead, unlike the moderate and life-sustaining climate on our planet.
Atmospheric conditions on Venus
The atmospheric conditions on Venus play a crucial role in its surface mapping. The thick atmosphere, combined with the runaway greenhouse effect, creates a significant challenge for exploration missions. The dense clouds of sulfuric acid reflect and scatter light, making traditional optical imaging ineffective. Thus, radar mapping techniques have been essential in studying Venus’ surface, as they are not hindered by atmospheric opacity.
Impact on surface mapping
The unique atmospheric conditions of Venus impact the way we map its surface. The inability to rely solely on optical imaging necessitates the use of alternative methods, such as radar, to overcome the challenges posed by the planet’s thick clouds and extreme temperatures. By utilizing these methods, scientists have achieved groundbreaking mapping results that have unveiled the geological intricacies of Venus’ surface.
Cartographic Insights
The detailed mapping of Venus has provided invaluable cartographic insights, shedding light on the planet’s geologic features, history, and potential changes over time.
Understanding surface features
By meticulously mapping Venus’ surface, scientists have gained a comprehensive understanding of its various landforms. From towering mountains to vast impact craters, the surface features painted by cartographic endeavors provide a visual representation of Venus’ geological diversity. These mappings have revealed the complex interactions of geological processes, such as volcanism and tectonics, shaping the planet’s surface.
Unraveling Venusian geologic history
The cartographic insights obtained from mapping Venus have allowed scientists to unravel the planet’s geologic history. By studying the distribution of impact craters and volcanic features, researchers can infer the age and timeline of various surface formations. These discoveries provide critical information about the processes that have shaped Venus over time and contribute to our understanding of the planet’s geological evolution.
Identification of volcanic hotspots
Volcanic activity is prominent on Venus, and thorough mapping has allowed scientists to identify volcanic hotspots on the planet’s surface. By pinpointing these hotspots, researchers can focus their attention on specific regions for further study and gain insights into the volcanic processes occurring on Venus. This information not only contributes to our knowledge of Venusian geology but also helps in refining our understanding of volcanic processes on other celestial bodies.
Detection of surface changes over time
The detailed maps of Venus have also enabled scientists to detect and analyze surface changes over time. By comparing images taken at different intervals, researchers can identify and study variations in surface features, such as fresh impact craters or changes in lava flow patterns. These observations provide valuable data on the dynamic nature of Venus’ surface and help to unravel the ongoing geological processes occurring on the planet.
Future Mapping Missions
The exploration and mapping of Venus are far from complete, with several upcoming missions set to further advance our knowledge of the planet. These missions will combine advanced imaging technologies, cartographic tools, and scientific objectives to continue mapping Venus in unprecedented detail.
Upcoming Venus exploration missions
NASA’s upcoming DAVINCI+ and VERITAS missions, along with the European Space Agency’s EnVision mission, are set to revolutionize our understanding of Venus. DAVINCI+ aims to study Venus’ atmosphere, while VERITAS will focus on mapping the planet’s surface using advanced radar systems. EnVision, on the other hand, will provide a comprehensive analysis of Venus’ geology and atmosphere. These missions will undoubtedly contribute to our ever-growing knowledge of Venus and its intricate nature.
Integration of advanced imaging technologies
The future mapping missions to Venus will integrate advanced imaging technologies to capture unprecedented detail and accuracy. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems will continue to play a crucial role in mapping Venus’ surface, allowing researchers to probe through the thick clouds and capture high-resolution images. Additionally, advancements in camera technologies and spectrometers will further enhance our ability to study the planet’s geologic features and atmospheric conditions.
Cartographic goals and objectives
The ultimate goal of future mapping missions to Venus is to create comprehensive and detailed maps of the planet’s surface. These maps will not only depict surface features but will also provide valuable information about Venus’ geologic history, volcanic activity, and tectonic processes. The integration of advanced imaging technologies and cartographic tools will ensure that these missions achieve their objectives efficiently and contribute significantly to our understanding of Venusian geology.
Mapping Venus Beyond Cartography
While mapping Venus has primarily focused on advancing our knowledge of its geology and surface characteristics, the data obtained from these efforts hold great potential for various other applications in planetary science and future human missions.
Applications of Venus mapping data
The mapping data collected from Venus provides a wealth of information that can be used for a variety of scientific applications. These data can aid in studying comparative planetology, allowing scientists to compare the geologic features of Venus with other celestial bodies, including Earth. Additionally, the mapping data can be utilized to model and simulate various planetary processes, further enhancing our understanding of the inner workings of rocky planets.
Contributions to planetary science
The detailed mapping of Venus contributes significantly to the field of planetary science. The data obtained from these efforts provide critical insights into the formation and evolution of planets, deepening our understanding of the geologic processes that shape them. By unraveling the mysteries of Venus, scientists can enhance their understanding of our own planet and other rocky bodies in the solar system.
Potential for future human missions
The mapping data and scientific knowledge gained from exploring Venus lay the groundwork for potential future human missions to the planet. Mapping the surface, understanding its geologic features, and studying atmospheric conditions are vital steps for assessing the feasibility and safety of human exploration. The advancements in cartography and high-resolution imaging technologies will play a crucial role in planning and executing future human missions, paving the way for humankind’s potential presence on Venus.
In conclusion, mapping Venus through high-resolution imaging and cartographic insights has significantly advanced our understanding of this intriguing planet. From past exploration missions like Venera and Magellan to the recent Venus Express mission, scientists have made remarkable discoveries about Venus’ geology and surface features. These mapping efforts, combined with technological advancements and future missions, hold great promise for unlocking the mysteries of Venus and contributing to our broader understanding of planetary science.